Infrared radiation
Infrared radiation (IR radiation for short) refers to light with wavelengths between 780 nm and 1 mm. IR radiation is divided into near IR (NIR, 780 to 1400 nm), mid IR (MIR, 1.4 to 15 µm) and far IR (FIR, 15 to 1000 µm).
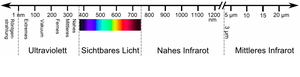 Spectral ranges from the UV to the MIR.
Spectral ranges from the UV to the MIR.
The CCD and CMOS cameras commonly used in image processing are sensitive up to the NIR range of around 1,050 nm. The spectral range visible to the human eye goes up to 780 nm. This means that the NIR range from 780 to 1,050 nm can be used for standard cameras with (invisible) infrared illumination. However, many cameras contain IR filters so that only the visible spectrum can be recorded, although these can usually be removed.
The disadvantage of IR radiation for measuring tasks is the lower resolution due to diffraction, which is also noticeable in the NIR.
Fields of application for NIR imaging: R&D, medical diagnostics, biometrics and access control, surveillance and industrial applications.
