Telecentric lighting
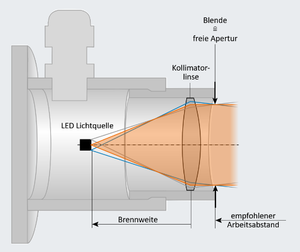
Telecentric illuminators (or collimated background or transmitted light illuminators or condenser illuminators or condensers) are optics whose light source (usually an LED) is projected to infinity, whereby a parallel beam path illuminates the object being measured. This results in improved edge detection in optical measurement technology and therefore greater measurement accuracy. Especially in combination with telecentric lenses, this reduces reflections and stray light at the edges of the object. The illuminated area and the light intensity remain the same regardless of the working distance.
Telecentric LED lighting could only be perfectly telecentric if the LED were a point-shaped light source with ideal radial beam characteristics. This is not feasible in practice. A telecentric error of around 0.2° can be achieved with the smaller lights with high-power LEDs. About 0.5° for medium sizes and about 1-2° for large telecentric illuminations.
 (Source: Sill)
(Source: Sill)
An increase in contrast is achieved by using short-wave light (blue instead of red light).
